Diabetes Mellitus is defined as a metabolic disorder of multiple aetiology characterised by a chronic state of hyperglycaemia (high blood sugar levels) with a disturbance of carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action or both. Insulin is a hormone and acts by inhibiting glucose production in the liver.
Diabetes has long term complications, the vast majority of complications in diabetes are due to damage to either large or small blood vessels. Fatty plaques (artheromas) are laid down in the blood vessels causing narrowing of the arteries and consequent poor blood flow and neuropathy – numbness, pain, tingling, swelling, and muscle weakness.
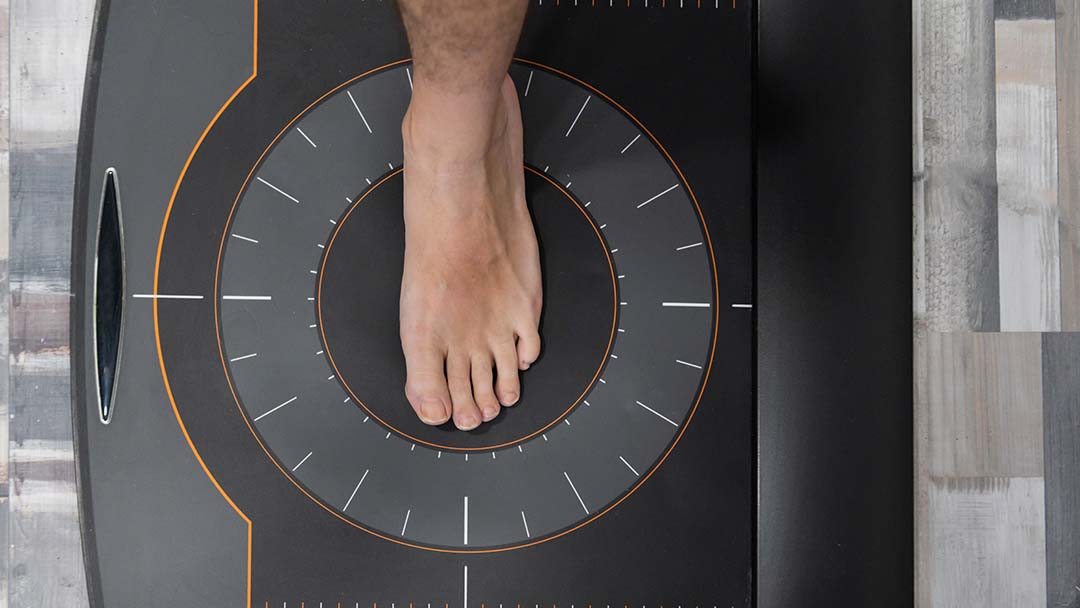
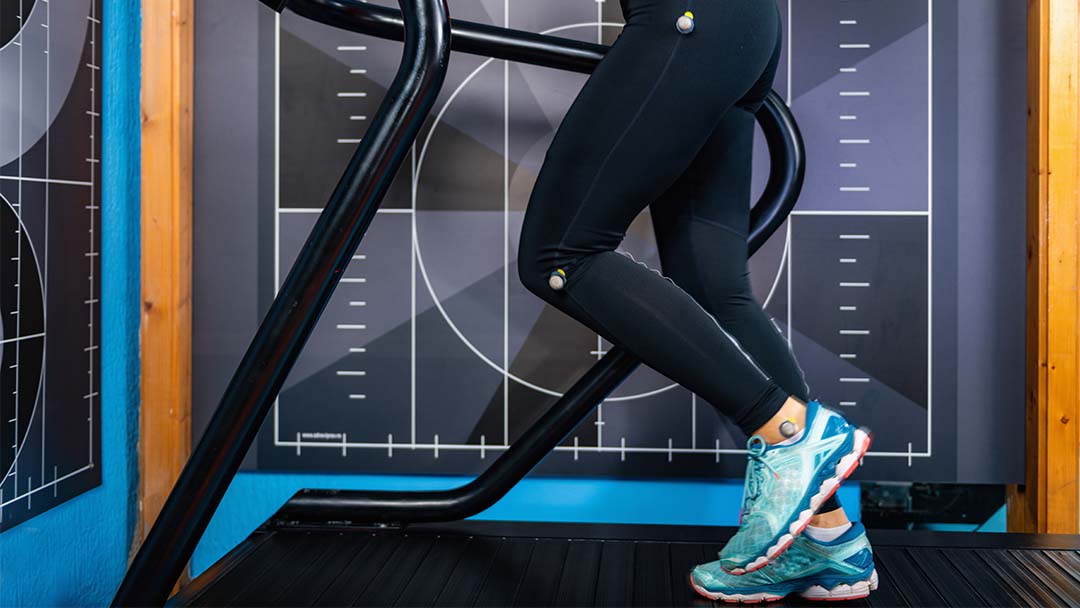
It is so important to support the diabetic foot with functional orthotics (shoe inserts) as this reduces the risk of ulcerations, slips, trips and falls and improves the natural walking pattern. There are two types of diabetic foot the neuropathic and ischaemic Foot, complications come when both types are present in the same foot.
Neuropathic foot
When the nerves to the foot are damaged the result is a warm, numb, dry and usually painless foot. The poor nerve supply to the foot leads to loss of sensation so that, if the surface of the skin is broken, the patient is unaware of the problem because of the inability to feel pain. Infection can easily enter forming an ulcer. Poor nerve supply can also result in damage to the muscles producing, for example, clawing of the toes and prominences of the metatarsal heads. These areas across the foot are not equipped to deal with extremely high amounts of pressure can also result in ulcer formation.
In the case of a neuropathic ulcer, expert attention from a podiatrist is required to debride any callus and remove the pressure on the affected area so that healing can take place. The latest research recommends that this is achieved with functional orthotics (shoe insoles).
Ischaemic Foot
Damage to the circulation to the foot leads to it being cold and painful with absent pulses. The ischaemic ulcer results from local pressure on an area poorly supplied with blood.
Useful websites for managing diabetes:
www.diabetes.org.uk – Diabetes UK is the largest organisation in the UK for people with diabetes.
(funding research, campaigning and helping people live with the effects of diabetes)
www.footindiabetes.org – A Journal for the prevention and management of diabetic foot disease.